Amazon Route 53 - How Internet Traffic Is Routed
The diagram below details how the process of resolving URLs to IP addresses takes place.
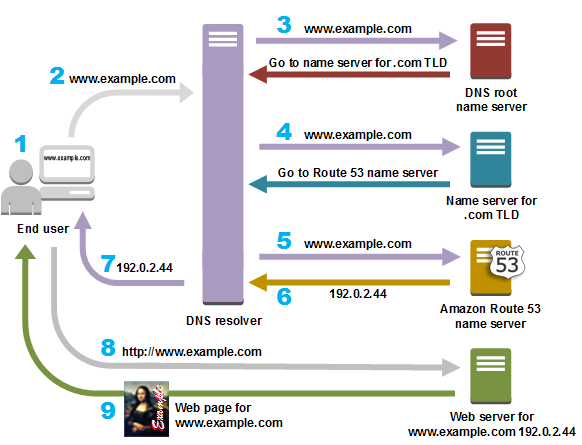
-
A user opens a web browser, type www.example.com in the address bar, and press Enter.
-
The request from www.example.com is routed to a DNS resolver, which is usually managed by the Internet Service Provider (ISP), such as a cable Internet provider, a DSL broadband provider, or a corporate network.
-
The ISP DNS resolver forwards the request from www.example.com to a DNS root name server.
-
The DNS resolver forwards the request from www.example.com again, this time to one of the TLD name servers of .com domains. The .com domain name server responds to the request with the names of the four Route 53 name servers associated with the example.com domain. The DNS resolver caches the four Route 53 name servers. The next time someone accesses example.com, the solver will skip steps 3 and 4 because it already has the name servers for example.com. Name servers are normally cached for two days.
-
The DNS resolver chooses a Route 53 name server and forwards the request from www.example.com to that name server.
-
The Route 53 name server looks for the record www.example.com in the hosted zone example.com, gets the associated value, such as the IP address of a web server, 192.0.2.44, and returns the IP address to the DNS resolver.
-
The DNS resolver finally has the IP address the user needs. The resolver returns the value for the web browser.
The DNS resolver also caches the IP address of example.com for a period that you specify. That way, it can respond faster the next time someone visits example.com. For more information, see time to live (TTL).
-
The web browser sends a request from www.example.com to an IP address it obtained from the DNS resolver. This is where your content is. For example, a web server that runs on an Amazon EC2 instance or an Amazon S3 bucket that is configured as a site endpoint.
-
The web server or other resource in 192.0.2.44 returns the web page from www.example.com to the web browser and the browser displays the page.
References: